What is a Fabric Recycling Machine and How Does It Benefit the Environment
In recent years, the fashion industry has faced increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental impact, predominantly due to the massive amounts of textile waste generated each year. As consumer awareness grows, innovative solutions are sought to mitigate this crisis, and one such technology making a significant impact is the fabric recycling machine. Designed to process a variety of textiles, these machines enable the efficient transformation of discarded clothing and materials into reusable fibers, significantly reducing waste sent to landfills.
Moreover, fabric recycling machines contribute to a circular economy by allowing resources to be reclaimed and repurposed, thus minimizing the demand for new raw materials. This sustainable approach not only conserves natural resources but also reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional textile production. By incorporating fabric recycling machines into waste management and production processes, individuals and organizations can play a crucial role in fostering a more environmentally responsible way of engaging with fashion. In doing so, they not only help to clean up the planet but also support the ongoing evolution of a more sustainable textile industry.

What is a Fabric Recycling Machine?
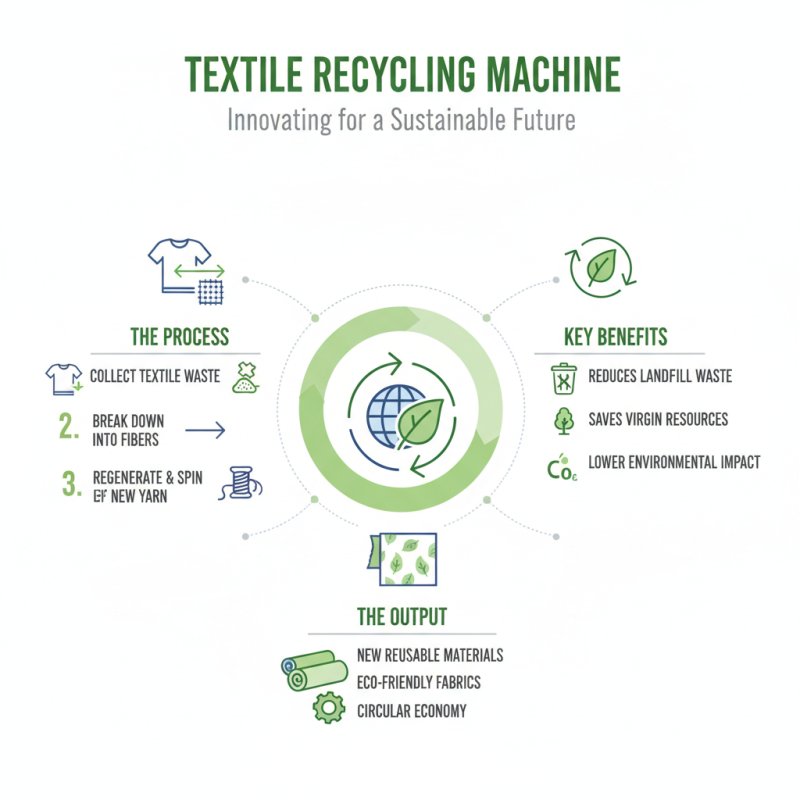
A fabric recycling machine is an innovative technology designed to process textile waste and convert it into reusable materials. These machines work by breaking down old fabrics, such as clothing and industrial textiles, into fibers that can be regenerated and spun into new yarns. This process not only reduces the need for virgin materials but also addresses the growing problem of textile waste in landfills.
The operation of a fabric recycling machine typically involves several stages. Initially, the unwanted or damaged fabrics are sorted and pre-processed to remove non-textile components like buttons or zippers. Following this, the fabrics are mechanically shredded and then subjected to various treatments to extract clean fibers. Depending on the machine's design, additional steps such as dye removal and fiber blending might occur, resulting in high-quality materials ready for production. This recycling method closes the loop in the textile industry, promoting sustainability and reducing the environmental impact associated with fabric production and disposal.
How Does a Fabric Recycling Machine Operate?
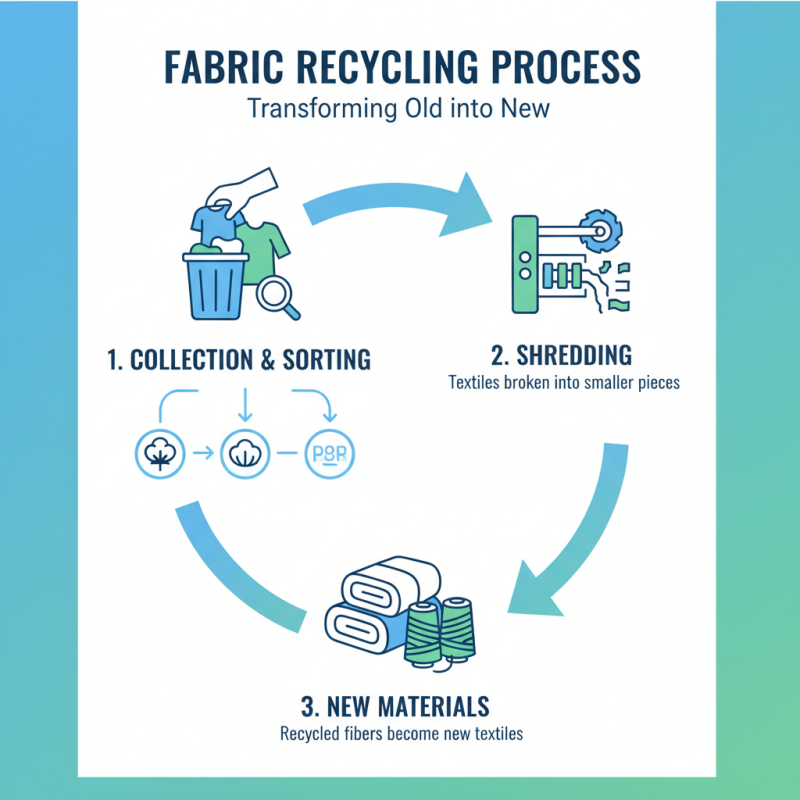
A fabric recycling machine operates through a systematic process designed to convert discarded textiles into reusable materials. The initial step involves collecting and sorting the fabrics, where different types of textiles are separated based on their composition, color, and condition. This sorting is crucial as it ensures that the recycling process runs efficiently and produces high-quality end products. Once sorted, the fabrics are shredded into smaller pieces, making them easier to process and allowing for a more uniform recycling outcome.
Following shredding, the extracted fibers undergo a cleaning process to remove impurities such as buttons, zippers, and dirt. Advanced fabric recycling machines employ various technologies like air classification and magnetic separation to effectively eliminate these contaminants. After cleaning, the fibers can be blended and reprocessed into new fabric materials or other products. This not only reduces waste in landfills but also conserves resources by decreasing the need for virgin materials in the textile industry. By transforming waste into valuable products, fabric recycling machines play a vital role in promoting sustainability and reducing the environmental footprint of the fashion and textile sectors.
Environmental Benefits of Fabric Recycling Machines
Fabric recycling machines play a crucial role in reducing textile waste, which is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally. By converting unwanted or discarded textiles into reusable raw materials, these machines significantly decrease the amount of fabric that ends up in landfills. A lesser-known fact is that the fashion industry is responsible for a large percentage of global pollution, primarily due to the energy-intensive processes involved in producing new fabrics and the environmental costs of waste disposal. By recycling textiles, we not only mitigate these effects but also conserve valuable resources such as water and energy that are otherwise consumed in the production of new materials.
Moreover, fabric recycling machines contribute to a circular economy by promoting the reuse of materials. This process helps in reducing the demand for virgin textiles, leading to lower carbon emissions associated with manufacturing and transport. The recycling process not only diverts waste but also creates sustainable job opportunities in the recycling sector. By encouraging the repair and repurposing of textiles, these machines help foster a more sustainable mindset among consumers, shifting focus towards conscious consumption and resource conservation. The environmental benefits extend beyond mere waste reduction; they play an essential role in preserving ecosystems, reducing pollution, and combating climate change.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional Waste Management vs. Fabric Recycling
The traditional waste management system often relies heavily on
landfills and
incineration, which pose
significant environmental risks. As textiles are one of the fastest-growing
waste streams globally, the disposal of fabric in landfills leads to harmful
greenhouse gas emissions and the loss of valuable resources.
Incineration, while reducing
waste volume, releases toxins into the atmosphere, affecting air quality and
public health. Therefore, this conventional approach is insufficient in
addressing the unique challenges posed by fabric waste.
In contrast, fabric recycling
presents a more sustainable solution. Fabric recycling machines efficiently break
down textiles into reusable fibers, significantly reducing waste destined for
landfills. This process not only conserves natural resources but also
minimizes harmful emissions associated with traditional disposal methods.
Furthermore, recycling fabric generates new economic opportunities by creating
jobs in the recycling sector, promoting a circular economy.
By transitioning to fabric recycling,
society can mitigate environmental damage while fostering innovation and
sustainability in waste management practices.
Future Innovations in Fabric Recycling Technology
The future of fabric recycling technology holds tremendous promise in addressing the growing textile waste crisis. As the fashion industry continues to expand, innovative solutions are being developed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of fabric recycling processes. One significant advancement is the introduction of systems that can automatically identify, sort, and break down various textile materials. These smart technologies utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to optimize the recycling process, ensuring that different types of fabrics are processed appropriately, which ultimately increases the recovery of valuable raw materials.
In addition to improved sorting methods, researchers are exploring enzymatic recycling methods that can break down polyester and other synthetic fibers at a molecular level. This biotechnological approach not only minimizes waste but also reduces the energy consumption associated with traditional recycling methods. Furthermore, innovations in chemical recycling are paving the way for the transformation of discarded textiles back into virgin-quality fibers that can be reused in new garment production. As these technologies continue to develop, they promise to close the loop in the textile lifecycle, fostering a more sustainable fashion industry while significantly benefiting the environment by reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources.
Related Posts
-

How to Effectively Use Textile Waste Recycling Machine for Sustainable Practices
-

Top 5 Fabric Weaving Machines: Revolutionize Your Textile Production Today!
-
Top 7 Direct to Fabric Printing Machines Revolutionizing Textile Production
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Industrial Fabric Laser Cutting Machines for Your Business
-

Top 10 Fabric Printing Machines for High Quality Custom Designs
-

2025 Top 10 Textile Printing Machines Revolutionizing the Industry
